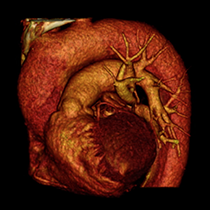
Pulmonary artery aneurysm
Is it a rare but severe condition, with an unknown prevalence. Le paucity of cases of PAA limits the understanding of disease progression and treatment options. Its natural outcome remain controversial as well. Occasionally sudden cardiac death occurred in asymptomatic patients. However in patients that received only conservative treatment and close monitoring a prolonged survival of more than 10 years have been observed.
PAA is commonly associated to congenital cardiac anomalies such as patent ductus arteriosus, ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, aortic valve hypoplasia, bicuspid aortic valve, pulmonary valve stenosis. PAA can also be secondary to pulmonary hypertension, Behcet’s disease, syphilis, tuberculosis, Marphan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
Clinical manifestations are non-specific (or absent) and include hemottisis, shortness of breath, chest pain, palpitations, syncope, cough, dyspnea, cyanosis, pneumonia.
CT pulmonary angiogram is the diagnostic test of choice for the diagnosis of PAA.
Currently there are no guidelines for the treatment of this pathology.
Treatment must be tailored according to the underlying causes.
DICOM VIEWER
AXIAL

CORONAL

SAGITTAL

Biomodels - STL files

Aorta
€9.99 VAT excluded
Pulmonary artery
€6.99 VAT excluded
Left atrium
€4.99 VAT excluded
Right atrium
€5.99 VAT excluded
Myocardium
€12.99 VAT excluded
Apex
€6.99 VAT excluded
Mitral valve
€14.99 VAT excluded
Tricuspid valve
€14.99 VAT excluded
Right heart
€11.99 VAT excluded
Left heart
€9.99 VAT excluded
Heart
€16.99 VAT excluded